DevOps Project: Build and push the image to DockerHub and run the container through Jenkins
In the fast-paced world of software development, efficiency is key. Developers strive to build, test, and deploy applications swiftly and reliably. This is where the powerful combination of Docker and Jenkins comes into play. Docker enables containerization, providing a consistent and isolated environment for applications to run, while Jenkins automates the entire software development lifecycle.
In this blog, we will delve into the integration of Docker and Jenkins to create a seamless development workflow that fosters collaboration, improves efficiency, and ensures the delivery of high-quality software.
Follow the below steps to install Jenkins on GCP VM(Linux)
- create a new VM, add a firewall rule to allow port 8080(for Jenkins), and click on SSH to connect to VM.

Install Java(pre-requisite) and Jenkins:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y openjdk-11-jdk
java –version
wget https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/binary/jenkins_2.332.3_all.deb
sudo dpkg -i jenkins_2.332.3_all.deb
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install jenkins
sudo systemctl start Jenkins
sudo service jenkins start
Jenkins runs on port 8080 by default. Open a web browser and navigate to http://<your-vm-ip>:8080 access the Jenkins web interface.
For getting the password, run this :
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
INSTALL DOCKER
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker.io
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo usermod -aG docker dockeruser
docker version
open below file
sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/dockeruser
Add this to file: dockeruser ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL
Add the Dockerfile to the git hub.

Start with Jenkins:
Install Plugins - Docker, docker step, cloudbees docker.
Add global credential for docker hub in Jenkins.

Login Docker hub from VM: cmd- docker login
Create a job in Jenkins - Pull the PHP website, and the Dockerfile from the git repo and build and push image to docker hub
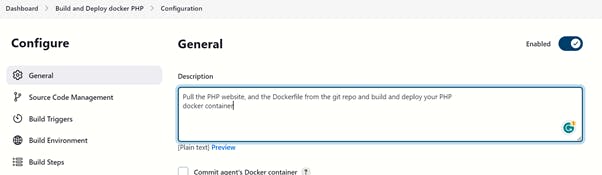
Add git repository

In the Build step, select Docker Build and Publish
Provide the repository of dockerhub: Repository Name formate - username/repo

Add the credential which was added to the global credential

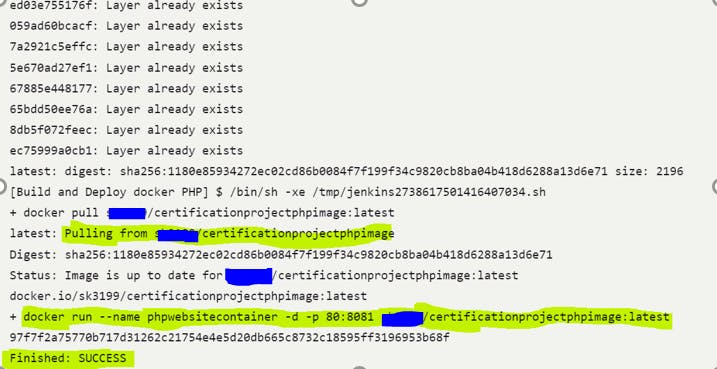
To run the container, Add the next build step and add execute the shell command and add these commands.

Save the configuration and run the build.
Check in the console output
Docker Hub:

Conclusion:
In conclusion, the seamless integration of these tools empowers developers to focus on crafting exceptional code, while automation takes care of the tedious and repetitive tasks. By containerizing applications with Docker, we ensure consistency across various environments, making deployment a breeze.
Jenkins' robust automation capabilities enable us to easily implement continuous integration and continuous delivery. This, in turn, fosters a culture of collaboration and rapid feedback, where engineers can confidently deliver changes to production without fear of breaking existing features. Happy Learning!